Aniracetam is a nootropic drug (ie brain enhancer) of the "racetam" chemical family.
First synthesized by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s, it is marketed as a prescription drug in Europe under many names, but can be purchased in the United States as a dietary supplement.
What Does Aniracetam Do?
As with many other racetam derivatives, it has been shown to enhance memory and cognition through a multitude of biochemical pathways.
This is ideal for anyone looking to improve mental function, whether you are a student cramming for an exam, or an adult yearning to regain the declarative sharpness of years prior.
Benefits of Aniracetam
The benefits of aniracetam run deep, and it's a main contender if you're considering taking something from the racetam family.
Memory Improvement
Through hippocampal and neocortical enhancement pathways. After consuming aniracetam, human participants improved their scores on multiple intelligence and memory tests. (3)
Enhanced "Executive Function"
by preferentially elevating levels of dopamine, serotonin and acetylcholine in the prefrontal cortex. (1)
Reduced anxiety
This has been shown in both human and animal models, as well as anecdotal information.
This is particularly promising since the most common pharmaceuticals currently prescribed for anxiety are benzodiazepines (such as Valium, Xanax, and Klonopin) that can cause nasty side effects with one meta-analysis finding "that long-term use of benzodiazepines was associated with moderate to large adverse effects on all areas of cognition." (2)
Aniracetam vs. Noopept
Noopept is also a nootropic that yields potentially anxiolytic effects. However, Aniracetam's seem stronger for this purpose, although Noopept may be more effective in other areas, as discussed in our Noopept blog post linked above.
Neuroprotection
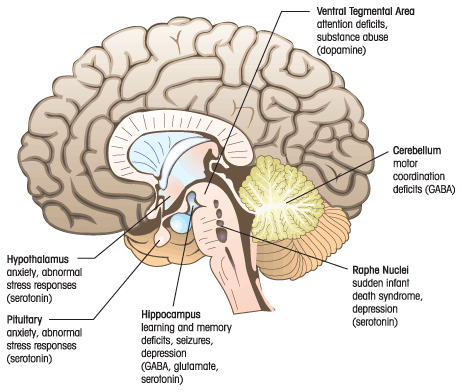
Aniracetam is Neuroprotective on the Brain
Many Other Benefits:
The above statements have been concluded from animal and human studies. But animal studies indicate that it may have therapeutic benefit for disorders such as:
- hypoattention
- hypovigilance-arousal
- impulsiveness
- hyperactivity
- fear and anxiety
- depression
- impaired rapid-eye movement sleep
- disturbed temporal regulation
- behavioral performance
- and even bladder hyperactivity (5)
It is important to note that these statements have not been approved by the FDA, and you should always consult your doctor before beginning any new diet and/or supplementation program.
These benefits may not apply to you, or may only be mild, and you may have underlying issues that render this compound ineffective.
Aniracetam vs. Piracetam
Piracetam is aniracetam's "parent compound", and was the first racetam discovered to have pronounced cognitive enhancements in animal and human subjects with an excellent safety profile.
Consequently, the discovery of piracetam compelled Dr. Corneliu E. Giurgea to coin the term nootropic, meaning a drug or supplement that enhances cognition while being neuroprotective or extremely nontoxic. Aniracetam is a nootropic under this definition.
Lower Dosing:
Aniracetam, unlike piracetam, is a hydrophobic molecule (fat-soluble) and is considerably more potent than its parent compound.
Anxiety Reduction:
Aniracetam has a pronounced anxiolytic effect by agonizing (enhancing) the effects of dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine in the brain.
- Animal studies indicate that it "preferentially increase extracellular levels of dopamine (DA) and serotonin (5-HT) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), basolateral amygdala and dorsal hippocampus of the mesocorticolimbic system." (1)
- Aniracetam's ability to reduce anxiety appears unique among other racetams.
Possible Biphasic Effects:
Unbeknownst to some, the primary cognition enhancing effects of aniracetam are caused by its main metabolites, 4-p-anisamidobutyric acid (ABA), 2-pyrrolidinone (PD) and p-anisic acid (AA). (8)
- This is important to note because although the purported half-life of aniracetam is only 1-2.5 hours, the lasting impact of its psychoactive metabolites confer day-long effects with 2-3 separate daily doses.
- Many individuals report that aniracetam displays biphasic effects, rendering an initial calming effect which is replaced by a more stimulating and focusing effect after a few hours, corresponding with its half-life.
How does aniracetam work?
Like all of the drugs of the racetam chemical class, the MOA (or mechanism of action) for aniracetam is complex and simply not fully understood. We will focus mainly on what is known.
Current pharmacological studies indicate that aniracetam works mainly through the modulation of cholinergic, glutamatergic, and monoaminergic neurotransmittion, the specifics of which are described below:
Cholinergic Mechanism:
Aniracetam Cholinergic Mechanism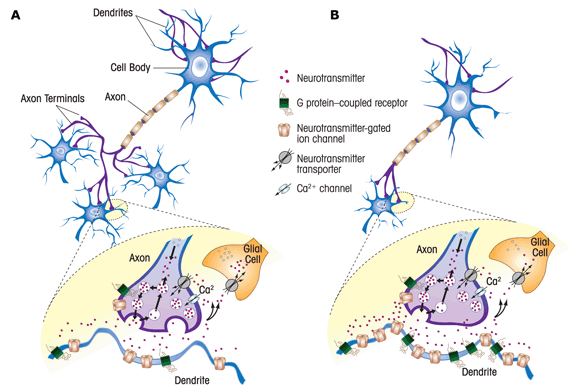
- But in the brain, acetylcholine is responsible for neural plasticity (memory formation), arousal, reward and sustained attention. Deficits in acetylcholine are found in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease. (6)
- Aniracetam, more specifically its metabolites, elevates levels of acetylcholine and preferentially amplifies the response of cholinergic systems in areas of the brain responsible for higher order cognition (the prefrontal cortex), and areas responsible for memory acquisition and utilization (the hippocampus).
- In animal studies, aniracetam rectified hippocampal and cerebral cortex acetylcholine reductions caused by age and brain damage. (5)
Glutamatergic Mechanism:
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter, causing synaptic plasticity which is essential for learning and memory. (11)
- Aniracetam acts as a 'positive allosteric modulator' of the glutamatergic AMPA and NMDA receptors, thus enhancing the efficacy of the glutamergic system within the hippocampus. (5)
Monoaminergic Mechanism:
Oral aniracetam elicits dopamine and serotonin release in the prefrontal cortex, dorsal hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala.
- These regions are essential in the regulation of emotion, mood, motivation, sleep-wakefulness, and cognition, strongly suggesting that aniracetam's positive effect on mood and anxiety are brought about by modulating this system.(5)
Aniracetam provokes a uniquely selective, yet cognitively holistic response. Many users report a lack of noticeable 'effects' -- but this is a good thing!
This means it lacks peripheral effects and has a high specificity for the brain (where very little sensory receptors exist).
One study using patas monkeys showed that aniracetam did not improve cognition on banal and simple tests of learning, but caused a substantial improvement when researchers increased the complexity of the task. (12)
This suggests that aniracetam shows its true colors when you really push your mental limits! It may not be for getting through boring, repetitive tasks quicker. It's for doing more brilliant things better.
Dosing: How to Take It
In animal studies, doses ranging from 10mg/kg to 100mg/kg have been assayed with efficacy.
Human trials suggest a dose of 1000-1500mg split into multiple doses per day, with food, although doses as low as 400mg have shown rise in blood aniracetam, and primary metabolite, levels. These statements are not approved by the FDA, and you should always consult your doctor before consuming this supplement.
To Take it with Fatty Foods or Not?
There is a whole lot of debate as to whether or not to take it with food, as it's fat soluble. Eggs are popular because they also contain choline.
However, contrary to what is commonly stated on other sources, consuming fatty foods with aniracetam (and all other fat-soluble drugs) does not necessarily aid with absorbtion.
In fact, excessive consumption of fats may actually cause the drug to have a reduced absorbtion (ie excreted fecally unchanged.)
Safety, Side Effects, and Dangers
Aniracetam Dosage and Side Effects
Aniracetam Safety:
Like other racetams, aniracetam is very safe; with an LD50 ( median lethal dose) of 4.5g/kg orally in rats and 5.0g/kg in mice, it is assumed a human would have to consume over 500 times the average daily dose of 1.5 grams to reach an equipotent LD50. (9)
We of course don't recommend coming anywhere near those numbers - 1.5g/day for a human is plenty.
- No animal studies have found toxic or teratogenic effects, and aniracetam does not influence food intake in rodents. (10)
- No drug interactions are known, and there have been no reported cases of overdose.
Tolerance and Withdrawal?
When given the option, monkeys will not self-administer aniracetam. And "after 31 days of daily dosing , no physical or behavioral withdrawal symptoms are observed upon discontinuation". (7)
Anecdotal information shows that there is very little to no noticeable withdrawal symptoms, although there are not several human studies mentioning this.
Potential Aniracetam Side Effects:
According the manufacturers insert for Draganon (European prescription for aniracetam):
Draganon is well tolerated by all patients, even the elderly. Although occasional signs of agitation, anxiety, unrest, insomnia have been reported, these side effects subside if treatment is modified. Rare side effects have been reported of headache, a sense of epigastric heaviness, drowsiness, asthenia and diziness. Should you experience any side effects not described here consult your physician. (13)
The Headache Factor: Scale Doses Gradually and Get Your Choline In!
As with choline supplements, one must note of the common headache side effects reported frequently with racetams. This specifically occurs if you do not gradually scale up your doses or take it with a choline product. Updated by Mike
So start at the minimum recommended dosage, and scale up over the course of a week or two. Additionally, it's best to take it with an acetylcholine precursor. This brings us to the next section:
Stacking: Supplements that synergize with Aniracetam
The nootropic potency of aniracetam can be enhanced by co-administration with acetylcholine precursors such as:
- Choline (choline bitartrate, choline citrate, and choline chloride)
- Lecithin
- DMEA
- Phosphatidylserine (PS)
- CDP-Choline
- Alpha GPC
- Centrophenoxine
- Acetyl-l-carnitine (ALCAR) acts as acetyl donor
Stacking aniracetam with other racetams (piracetam, pramiracetam, oxiracetam, etc.) is reported to have synergistic nootropic effects. This may get costly, so racetam users typically like to find their "favorite" one that works best, and stick with it.
Where to Buy Aniracetam
Buying nootropics is a tricky subject -- even more so when dealing with the racetams. Due to FDA compliance, stores and brands seem to come and go.
This site (PricePlow.com) is not a store, it is a price comparison engine. We will do our best to link you to trusted stores where you can buy it online, such as the preferred form linked below.
You will almost certainly not be able to find this at a local retail store such as GNC or Vitamin Shoppe - you'll have to buy online through a trusted store with us.
What is the Best Aniracetam?
Our current preferred powder is Peak Nootropics Aniracetam. It is a powder that comes in 50 or 100g packages, and the price and quality can't be beaten.
Sources Cited
1. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11597608
2. https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165%2F00023210-200418010-00004
3. (Saletu, 1980, 1984). https://www.smart-publications.com/books/full-text/smart-drugs-and-nutrients/smart-drugs-and-nutrients-sec4/smart-drugs-and-nutrients-sec4-aniracetam
4. Neurosci Lett. 2003 Mar 27;339(3):187-90. Effects of Aniracetam on extracellular levels of transmitter amino acids in the hippocampus of the conscious gerbils: an intracranial microdialysis study. Yu S, Cai J. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12633884
5. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1527-3458.2002.tb00216.x/pdf
6. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926641000000124
7. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1987 Jan;89(1):33-46. [Drug dependence test on a cerebral insufficiency improver, aniracetam] [Article in Japanese]. Kuwahara A, Kubota A, Hakkei M, Nakamura K. https://www.hflsolutions.com/ne/ingredients/aniracetam.shtml
8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10784432
9. Gouliaev AH, Senning A. Piracetam and other structurally related nootropics. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1994 May;19(2):180-222. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8061686
10. Lancet. 2001 Dec 1;358(9296):1885-92. Pyrrolidone derivatives. Shorvon S. https://sciencelinks.jp/j-east/article/200010/000020001000A0335175.php
11. McEntee, W. J.; Crook, T. H. (1993). "Glutamate: Its role in learning, memory, and the aging brain". Psychopharmacology 111 (4): 391–401. doi:10.1007/BF02253527 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7870979
12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7667-71. 7-Chloro-3-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine S,S-dioxide (IDRA 21), a congener of aniracetam, potently abates pharmacologically induced cognitive impairments in patas monkeys. Thompson DM, Guidotti A, DiBella M, Costa E. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC21283/
13. https://www.erowid.org/smarts/aniracetam/aniracetam_info1.shtml
