Metabolic BioShock is a now-discontinued pre-workout from Giant Sports.
This formula is one of the most exciting to hit supplement shelves because of its unique formula. It is truly a comprehensive product with a distinctive approach to pre-workout supplementation. Creating Metabolic BioShock makes Giant Sports a welcome addition to an industry full of imitators.
More than just energy

Metabolic BioShock
An area of particular note for this formula is that it bucks the one-upmanship trend that is ubiquitous with supplement manufacturers who consistently produce stimulant blends that more closely resemble party drugs than something you want to take before heading to the gym. That's not to say that BioShock is stim free. In fact, there's a hefty dose of caffeine and some other mild energy enhancers inside. But what you won't find are shady, questionably legal stimulant analogues or illicit substances.
Pre-workout plus
The formula is completely open-label so you know exactly what you're getting with each scoop.
You might scratch your head at first when you look at the ingredients panel. You'll see a lot of vitamins and minerals that boost bone and immune health, and then other compounds that don't seem to have anything to do with exercise. That's because Giant Sports is going in an unexpected direction -- especially compared to other companies.
Giant Sports is aiming for an overall health formula that doesn't just try to enhance the acute physical results of your workout, but rather, strives to benefit all areas that surround your workout.
Many essential vitamins and minerals are depleted during strenuous exercise, which can lead to deficiency. But Metabolic BioShock has you covered. Exercise can also put a lot of stress on your bones and joints, but Metabolic BioShock has you covered there, too. Just calling this product a pre-workout might be selling it short because it truly transcends the pre-workout category of supplementation.
100% open label
Proprietary blends are seen as a necessary evil by some companies to protect their formulas. But the concept is often abused to hide shoddily-dosed formulas behind ambiguous label tricks. There's no duplicity here. The formula is completely open-label so you know exactly what you're getting with each scoop.
High quality branded ingredients
If you take a look at the label you'll notice many trademarked ingredients, such as Opti-MSM, TRAACS, and NO3-T. Wherever possible, Giant Sports has elected to sell high quality branded ingredients from reputable suppliers. Many companies attempt to cut costs and duck paying license fees on patented ingredients by buying raw materials from shady suppliers with dubious quality control measures. Not this formula.
Ingredients
...it truly transcends the pre-workout category of supplementation.
The massive open-label formula, weighing in at a hefty 15g per scoop, is a mouthful. It contains 19 different ingredients. When taking the two-scoop maximum dose, you're consuming a whopping 30g of workout enhancement. It's worth noting that BioShock is carb-free since many big blend pre-workout formulas contain copious amounts of carbohydrate fillers.
Now lets dig into the label and see what's inside. For the purposes of this review, we're going to assume that you're working your way up to the maximum two-scoop dose, as that's how the product was formulated to be most optimally utilized.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are a big part of what makes this formula so unique. Americans are largely deficient in many of these nutrients and athletes are at even higher risk since they experience significant vitamin and mineral depletion during exercise. For that reason, those who workout or exercise often have higher vitamin and mineral requirements compared to the general population.
The inclusion of these ingredients is a great move by Giant Sports.
Calcium pantothenate - 1000mg (calcium [168mg] + vitamin B5 [830mg])
Vitamin B5 can enhance oxygen utilization during exercise as well as reduce lactic acid buildup. Calcium pantothenate as a mineral/vitamin salt also experiences significantly higher stability and absorption through the digestive system. Additionally B vitamins are vital for metabolizing fat and carbohydrates during exercise. Vitamin B5, specifically, produces fewer side effects in high doses compared to other B vitamins.
Like other minerals, calcium is depleted during endurance exercise, which can harm bone density. According to recent studies[1,2] calcium supplementation prior to working out can attenuate depletion, thereby preserving bone health.
Sodium glycerophosphate - 500mg
Sodium is an important electrolyte and aids in signal transmission throughout the body. Just like calcium, it is depleted during strenuous activity. While dietary sodium may have a bad reputation for its effects on blood pressure and heart health, the mineral actually plays an important role in hydration. Losing too much sodium, which is a real risk during prolonged workouts, can cause debilitating muscle cramps.
The glycerophosphate compound of sodium is in the formula because phosphates function as lactic acid buffers and reduce muscle soreness, resulting in enhanced endurance.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - 180mg
Extra vitamin C is beneficial to your workout in a variety of ways. Also known as ascorbic acid, vitamin C is another essential nutrient that can be depleted during exercise, which can cause fatigue. Supplementation with vitamin C has been shown to reduce this side effect during exercise[3]. Additionally, as Metabolic BioShock contains nitrates, another key benefit of Vitamin C is that it blocks the body's creation of harmful nitrate byproducts, called nitrosamines.[4] Vitamin C has also been shown to reduce muscle soreness after exercise.[5]
Vitamin D (cholecalciferol) - 2000IU
About one third of Americans are deficient in Vitamin D, which is no surprise since research suggests that the Institute of Medicine's RDA, at 400 to 800 IU, is significantly lower than necessary.[7] Intake of around 2,000IU has been shown to be ideal, with a safe tolerable limit of as much as 10,000IU daily.[6]
Vitamin D positively affects several areas BioShock targets for enhancement. Higher vitamin D metabolite levels are linked to increased muscle strength, improved bone mineral density, and increased vitamin K and calcium absorption[8, 9, 10, 11].
Vitamin K (phylloquinone) - 1mg
Vitamin K is an essential nutrient, but it isn't an acknowledged deficiency risk by the Centers for Disease Control. So why the inclusion? While the RDA is adequate for preventing acute bleeding associated with vitamin K deficiency, a newer study on atherosclerosis[45] indicates that long-term, non-severe deficiency can have negative effects on artery health. Additionally, when supplemented beyond the official daily requirements, the vitamin has a significant positive impact on bone and joint health and synergizes well with vitamin D.[10,12]
Zinc - 50mg (as TRAACS(R), zinc bisglycinate chelate)

Zinc
Another mineral depleted by exercise[13], zinc is an essential nutrient that is beneficial to a large number of bodily functions. While most are not specifically related to exercise, replacing depleted zinc fits in very well with the theme of Metabolic BioShock as an overall health enhancer -- not simply a pre-workout muscle builder.
Amino acids
Often included in pre-workouts for their manyfold positive effects on exercise, amino acids are a huge part of the Metabolic BioShock formula, making up over half of each scoop.
BCAAs (4:1:1 L-leucine: L-isoleucine: L-valine) - 6300mg
These three ingredients are well-known branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) that make up a substantial portion of muscle fiber. They also significantly boost the anabolic response to exercise via increased muscle protein synthesis and significant endurance boosts.
Glutamine nitrate - 1000mg
Glutamine has gotten a lot of bad press in recent years. Its purpose in this formula, however, is to bring nitrates into the formula. Nitrates are gaining popularity in the supplement industry thanks to several studies demonstrating significant positive effects on endurance, blood flow, oxygen efficiency, and vasodilation.
We're huge fans of nitrates, and many of the best products on the market use them. [14,15,16,17,18]
Taurine - 4000mg
Taurine is an amino acid that has been shown to enhance endurance exercise performance alone, and in combination with other amino acids.[19, 20] Additionally, taurine can boost blood flow, which means better absorption and nutrient delivery while you exercise.[21]
L-aspartic acid - 4000mg
Exercise-induced stress elevates ammonia levels in the blood, which can lead to fatigue.[40] One primary function of L-aspartate is to scavenge ammonia from the blood[39], help delay the onset of fatigue, and enhance endurance levels.
L-tyrosine - 1500mg
Tyrosine is an amino acid utilized as a precursor to noradrenaline and dopamine production -- key adrenergic hormones.[22] Additionally, it enhances cognition and reduces anxiety during times of acute stress, such as a gruelling workout. [23,24]
Stimulants
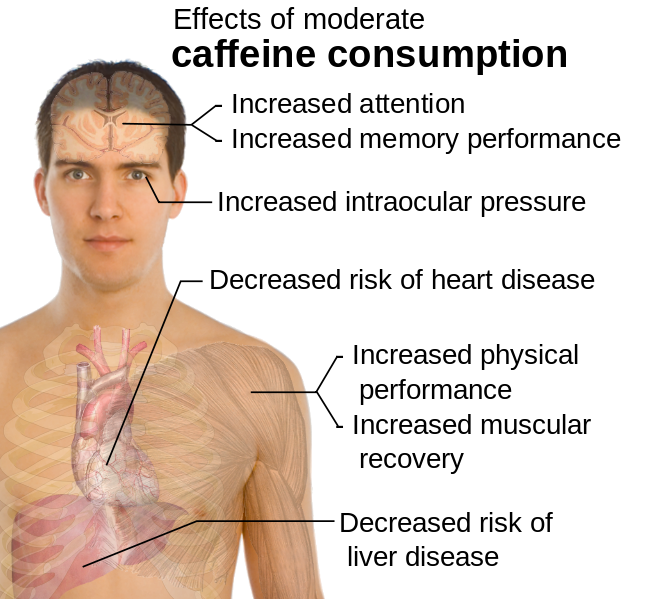
Caffeine Consumption
Caffeine - 300mg
Caffeine is the most widely used stimulant in the world, with dozens of studies backing up its performance enhancement effects. Caffeine consumption has been shown to:
- Increase power output[25]
- Oxidate fat[26]
- Improve metabolic rate[27]
- Increase endurance[28]
Taking 300mg of caffeine may sound like a large dose (equivalent to about three cups of coffee), but overall, Metabolic BioShock is light on stimulant content. So this will provide a nice kick for most people without being over the top. Just be sure to gradually work up to the full two-scoop dose, which will help build your tolerance.
Bai Mudan(TM) Fujian white peony tea (Camelia sinensis) extract - 40mg
Tea extracts as a category have a variety of positive effects due to catechin content.[30] Catechins can increase fat loss and fat oxidation while providing a modest energy boost. White tea, specifically as included in BioShock, has the highest levels of GABA, a relaxing neurotransmitter.[29]
Performance enhancing fundamentals
Creatine monohydrate - 2000mg & magnesium creatine chelate - 1000mg (creatine Magnapower(R))
Creatine is one of the most well researched performance enhancers on the market. It's utilized as a part of the ATP cellular energy generation process leading to profound increases in endurance and muscle building. You might be wondering why a gram (1000mg) of MCC was included. We surmise it's for the magnesium content. Magnesium is another essential mineral that vigorous exercise depletes.
L-carnitine-L-tartrate - 2000mg (Carnipure(R))
Carnitine is a key component of energy metabolism. This specific form is added to Metabolic BioShock because LCLT has the fastest uptake time of all forms of carnitine.[34] The compound is capable of reducing lactic acid buildup[31], reducing exercise-induced muscle damage[32], and enhancing nitric oxide production[33].
Joint support and antioxidants
The inclusion of powerful joint protection ingredients in Metabolic BioShock is another area in which the formula is superior to competing products.
Methylsulfonylmethane - 3000mg (Opti-MSM(R))
Good luck pronouncing that one! Another of the formula's overall health-promoting ingredients, this compound provides anti-inflammatory joint health benefits[35] and helps reduce muscle soreness[36].
Glucosamine HCL - 1500mg
Rounding out the joint-support ingredients, we have glucosamine, which can reduce joint inflammation and pain.[37, 38]
Stilbenox(TM) Vitis vinifera extract - 70mg
Vitis vinifera (grape vine) extract has potent antioxidant properties.[41] A surge in exercise-induced oxygen consumption can lead to increased free radical generation, which leads to fatigue, muscle damage, and limited exercise endurance. Antioxidants help remove free radicals from the body and may increase endurance and recovery levels.[42]
Q-20(TM) water solubilized coenzyme Q10 - 100mg
Coenzyme Q10 is another antioxidant that can aid exercise performance for reasons previously mentioned. It has a number of other beneficial properties related to cellular energy metabolism and vasodilatory function.[43, 44]
Directions for use

Metabolic BioShock Giant Sports
As directed, start with one scoop. For maximum effect, work your way up to two scoops. The powder mixes well with just a few shakes and tastes great. To avoid settling, give it another shake or two.
Safety
All of the ingredients in Metabolic BioShock are generally safe and tolerated by most people. As with supplements in general, you should check with your doctor prior to beginning supplementation and carefully review any potential allergies or negative drug interactions with prescription and over-the-counter medicines.
Where to buy
We scour the web and keep you informed of the best prices available. So check out our price comparison information on this page and sign up for our newsletter to find out about future deals and price drops.
References
- Barry DW; Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise;" Acute calcium ingestion attenuates exercise-induced disruption of calcium homeostasis;" 2011
- Nathan Gray; NutraIngredients.com; "Timing is Everything: Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements Before Exercise may Aid Bone Response;" 2013
- Huck CJ; Nutrition. "Vitamin C status and perception of effort during exercise in obese adults adhering to a calorie-reduced diet;" 2013
- Mirvish SS, et al; Science; "Ascorbate-nitrite reaction: possible means of blocking the formation of carcinogenic N-nitroso compounds; 1972
- 5. Bryer SC, Goldfarb AH; International Journal of Sport Nutrtion and Exercise Metabolism; "Effect of high dose vitamin C supplementation on muscle soreness, damage, function, and oxidative stress to eccentric exercise;" 2006
- Vieth R; American Journal of Clinical Nutrition; "Vitamin D supplementation, 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations, and safety;" 1999
- Grant WB, Holick MF; Alternative Medicine Review; "Benefits and requirements of vitamin D for optimal health: a review;" 2005
- Grimaldi AS, et al; Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise; "25(OH) vitamin D is associated with greater muscle strength in healthy men and women;" 2013
- Matsumoto T, et. al.; Bone; "Stimulation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 of in vitro mineralization induced by osteoblast-like MC3T3-E1 cells;" 1991
- Kidd PM; Alternative Medicine Review; "Vitamins D and K as pleiotropic nutrients: clinical importance to the skeletal and cardiovascular systems and preliminary evidence for synergy;" 2011
- Heaney RP; Journal of the American College of Nutrition; "Calcium absorption varies within the reference range for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D;" 2003
- Braam LA; Calcified Tissue International; "Vitamin K1 supplementation retards bone loss in postmenopausal women between 50 and 60 years of age;" 2003
- Micheletti A; Sports Medicine; "Zinc status in athletes: relation to diet and exercise;" 2001
- Larsen FJ, et. al.; Acta Physiologlica; "Effects of dietary nitrate on oxygen cost during exercise;" 2007
- Lansley KE; Journal of Applied Physiology; "Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of walking and running: a placebo-controlled study:" 2011
- Bailey SJ, et. al.; Journal of Applied Physiology; "Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high-intensity exercise in humans;" 2009
- Besc?s R, et, al.; Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise; "Acute administration of inorganic nitrate reduces VO(2peak) in endurance athletes;" 2011
- Fulford J.; Pflugers Archive; "Influence of dietary nitrate supplementation on human skeletal muscle metabolism and force production during maximum voluntary contractions;" 2013
- Ra SG; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; "Additional effects of taurine on the benefits of BCAA intake for the delayed-onset muscle soreness and muscle damage induced by high-intensity eccentric exercise;" 2013
- Rutherford JA, et. al.; International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism; "The effect of acute taurine ingestion on endurance performance and metabolism in well-trained cyclists;" 2010
- Moloney MA, et. al.; Diabetes & Vascular Disease Research; "Two weeks taurine supplementation reverses endothelial dysfunction in young male type 1 diabetics;" 2010
- Nakashima A, et. al.; Journal of Neural Transmission; "Role of N-terminus of tyrosine hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of catecholamines;" 2009
- Banderet LE, Lieberman HR; Brain Research Bulletin; "Treatment with tyrosine, a neurotransmitter precursor, reduces environmental stress in humans;" 1989
- Deijen JB, Orlebek JF; Brain Research Bulletin; "Effect of tyrosine on cognitive function and blood pressure under stress;" 1994
- Astorino TA, et, al.; Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise; "Effect of two doses of caffeine on muscular function during isokinetic exercise;" 2010
- Keijzers GB, et. al.; Diabetes Care; "Caffeine can decrease insulin sensitivity in humans;" 2002
- Astrup A, et. al.; American Journal of Clinical Nutrition; "Caffeine: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of its thermogenic, metabolic, and cardiovascular effects in healthy volunteers;" 1990
- Duncan MJ, Oxford SW; Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research; "The effect of caffeine ingestion on mood state and bench press performance to failure;" 2011
- Zhao M, et. al.; Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry; "Determination and comparison of ?-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content in pu-erh and other types of Chinese tea;" 2011
- Unachukwu UJ; Journal of Food Science; "White and green teas (Camellia sinensis var. sinensis): variation in phenolic, methylxanthine, and antioxidant profiles;" 2010
- Volek JS; American Journal of Physiology, Endocrinology and Metabolism; "L-Carnitine L-tartrate supplementation favorably affects markers of recovery from exercise stress;" 2002
- Kraemer WJ, et. al.; Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research; "The effects of L-carnitine L-tartrate supplementation on hormonal responses to resistance exercise and recovery;" 2003
- Bloomer RJ, et. al.; Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition "Glycine propionyl-L-carnitine increases plasma nitrate/nitrite in resistance trained men;" 2007
- Eder K, et. al.; International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrion Research; "Free and total carnitine concentrations in pig plasma after oral ingestion of various L-carnitine compounds;" 2005
- Feng L, et. al.; The Journal of Clinical Investigation "Involvement of reactive oxygen intermediates in cyclooxygenase-2 expression induced by interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and lipopolysaccharide;" 1995
- Kalman DS; Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition; "Influence of methylsulfonylmethane on markers of exercise recovery and performance in healthy men: a pilot study;" 2012
- Chopra A, et. al.; Rheumatology; "Ayurvedic medicine offers a good alternative to glucosamine and celecoxib in the treatment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, controlled equivalence drug trial;" 2013
- Herrero-Beaumont G, et. al.; Arthritis and Rheumatism; "Glucosamine sulfate in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study using acetaminophen as a side comparator;" 2007
- Sikorska H, et. al.; Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski; "Physiological functions of L-ornithine and L-aspartate in the body and the efficacy of administration of L-ornithine-L-aspartate in conditions of relative deficiency;" 2010
- Casa H, et. al.; Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry; "Increased blood ammonia in hypoxia during exercise in humans;"
- Torres JL, et. al.; Journal Agricultur Food Chemistry; "Valorization of grape (Vitis vinifera) byproducts. Antioxidant and biological properties of polyphenolic fractions differing in procyanidin composition and flavonol content;" 2002
- Lafay S, et. al.; Journal of Sports Science and Medicine; "Grape extract improves antioxidant status and physical performance in elite male athletes;" 2009
- Gao L, et. al.; Atherosclerosis; "Effects of coenzyme Q10 on vascular endothelial function in humans: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials;" 2012
- Nohl H, et. al.; Annals New York Academy if Science; "The biochemical, pathophysiological, and medical aspects of ubiquinone function;" 1988
- Berkner KL, Runge KW; Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; "The physiology of vitamin K nutriture and vitamin K-dependent protein function in atherosclerosis;" 2004



